Variable Creation allows you to define a formula using 1 or more selected variables and basic operators.
To create a variable, first name it.
Then begin typing the first part of the formula and you should see a list of relevant options. Select what you're looking for then add any operations and additional variables.
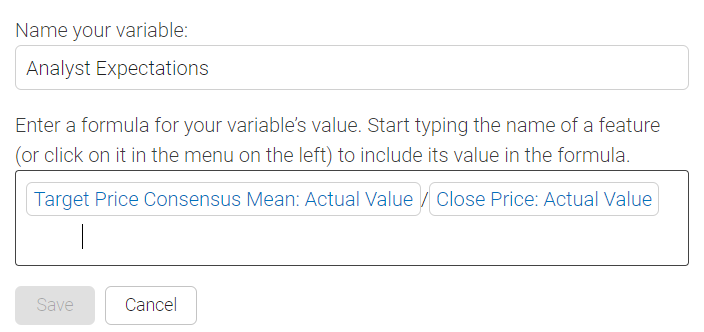
The variable creation process allows you to create your own custom variables through the use of standard mathematical operators and data from the variable selection page.
For example, you could create a formula with some concept of relative momentum to the benchmark: “Relative Momentum”: pct(Close Price: actual value, 21) - pct(benchmark(), 21)

The above function calculates the 21 day percentage difference in Close Price for each individual security in the universe and subtracts the 21 day percentage change of the benchmark.
Therefore if AAPL was $200 21 days ago and is $220 today, then the value for pct(Close Price: actual value, 21) would be 0.10.
Then the benchmark was SPY and it was $300 21 days ago and $303 today then its value would be 0.01.
The total result of the formula (for AAPL) would be 0.10 - 0.01 = 0.09.
You can create even more complex formulas using the functions detailed below.
Custom Functions:
1. Price of the Benchmark
Get Benchmark Price Time Series values using the benchmark for this particular model (set on the model creation “constraints” screen) and the price type (ie open price).
Syntax:
benchmark()
Parameters:
None
2. Apply Absolute Value
Apply absolute value on equation in function
Syntax:
abs(equation)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply absolute value upon
3. Apply Natural Logarithm
Apply natural logarithm on equation in function
Syntax:
log(equation)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply natural logarithm upon
4. Retrieve Minimum
Of the two equations retrieve the minimum of the two.
Syntax:
min(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation to compare to equation_2 to determine the minimum
equation_2 * - custom equation to compare to equation_1 to determine the minimum
5. Retrieve Maximum
Of the two equations retrieve the maximum of the two.
Syntax:
max(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation to compare to equation_2 to determine the maximum
equation_2 * - custom equation to compare to equation_1 to determine the maximum
6. Apply Exponent
Apply an exponent to the equation in the function
Syntax:
pow(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is used as the base in the exponentiation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is used as the exponent in the exponentiation
7. Apply Variance
Apply variance on the equation in the function
Syntax:
var(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply variance upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window when calculating variance
8. Apply Percent Change
Apply percent change over time to equation in function
Syntax:
pct(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply percent change upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window for calculating percent change
9. Apply Simple Moving Average
Apply simple moving average on the equation in the function
Syntax:
sma(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply simple moving average upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window when calculating simple moving average
10. Apply Weighted Moving Average
Apply weighted moving average on the equation in the function
Syntax:
wma(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply weighted moving average upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window when calculating weighted moving average
11. Apply Exponential Moving Average
Apply exponential moving average on the equation in the function
Syntax:
ema(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply exponential moving average upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window when calculating exponential moving average
12. Replace NaN (Not a Number)
Replace NaN in one equation based on the values in the other equation
Syntax:
nan_to_num(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is viewed for replacing NaNs
equation_2 * - custom equation that is used to replace the NaNs in equation_1. This could be a decimal if a constant value is sufficient.
13. Use historical data
Apply a lag to the data
Syntax:
prev(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply lag upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window for the lag
14. Use future data - ONLY USE IN CUSTOM GOAL EQUATIONS
Apply a lead to the data
Syntax:
fwd(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply lead upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window for the lag
15. Retrieve Minimum Over Time
Of the two equations retrieve the minimum of the two.
Syntax:
tmin(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply lead upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window for finding the minimum
16. Retrieve Maximum Over Time
Of the two equations retrieve the maximum of the two.
Syntax:
tmax(equation, num_days)
Parameters:
equation * - custom equation to apply lead upon
num_days * - number of business days to use as time window for finding the maximum
17. Boolean Greater Than or Equal To (>=)
Compare two equations with greater than or equal to boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
ge(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
18. Boolean Greater Than (>)
Compare two equations with greater than boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
gt(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
19. Boolean Equal To (==)
Compare two equations with equality to boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
eq(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
20. Boolean Not Equal To (!=)
Compare two equations with not equality boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
ne(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
21. Boolean Lesser Than or Equal To (<=)
Compare two equations with lesser than or equal to boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
le(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
22. Boolean Lesser Than (<)
Compare two equations with lesser than boolean logic and convert True/False to 1/0
Syntax:
lt(equation_1, equation_2)
Parameters:
equation_1 * - custom equation that is on the left hand side of the boolean equation
equation_2 * - custom equation that is on the right hand side of the boolean equation
